-
Bahasa Indonesia
-
English
Oleh: Vincent Gaspersz, Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt
American Society for Quality (www.asq.org) CMQ/OE, CQA, CSSBB, CQE, CQIA
American Production and Inventory Control Society (www.apics.org) CFPIM, CSCP
International Quality Federation (www.iqf.org) Six Sigma Master Black Belt
Registration Accreditation Board (www.exemplarglobal.org) Quality Management System Practitioner
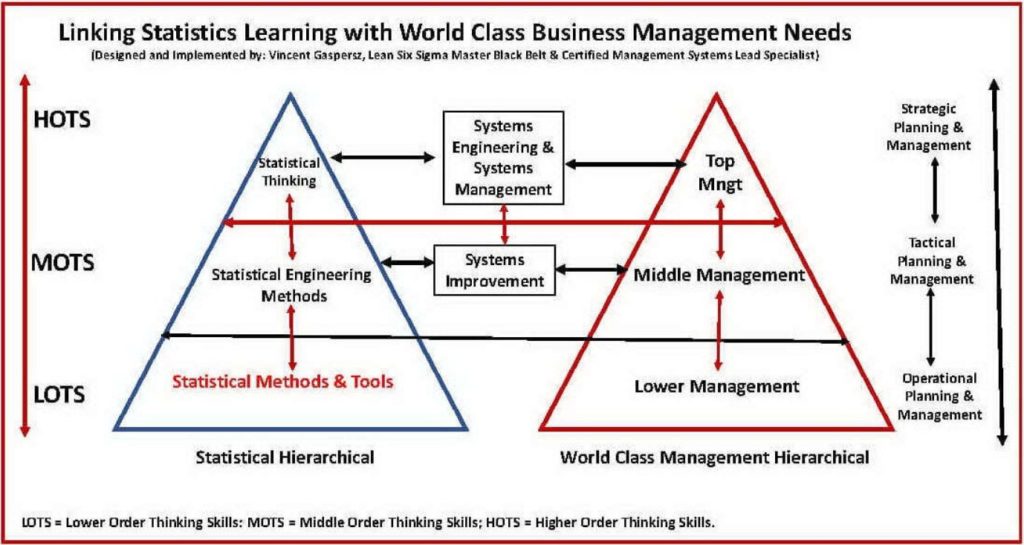
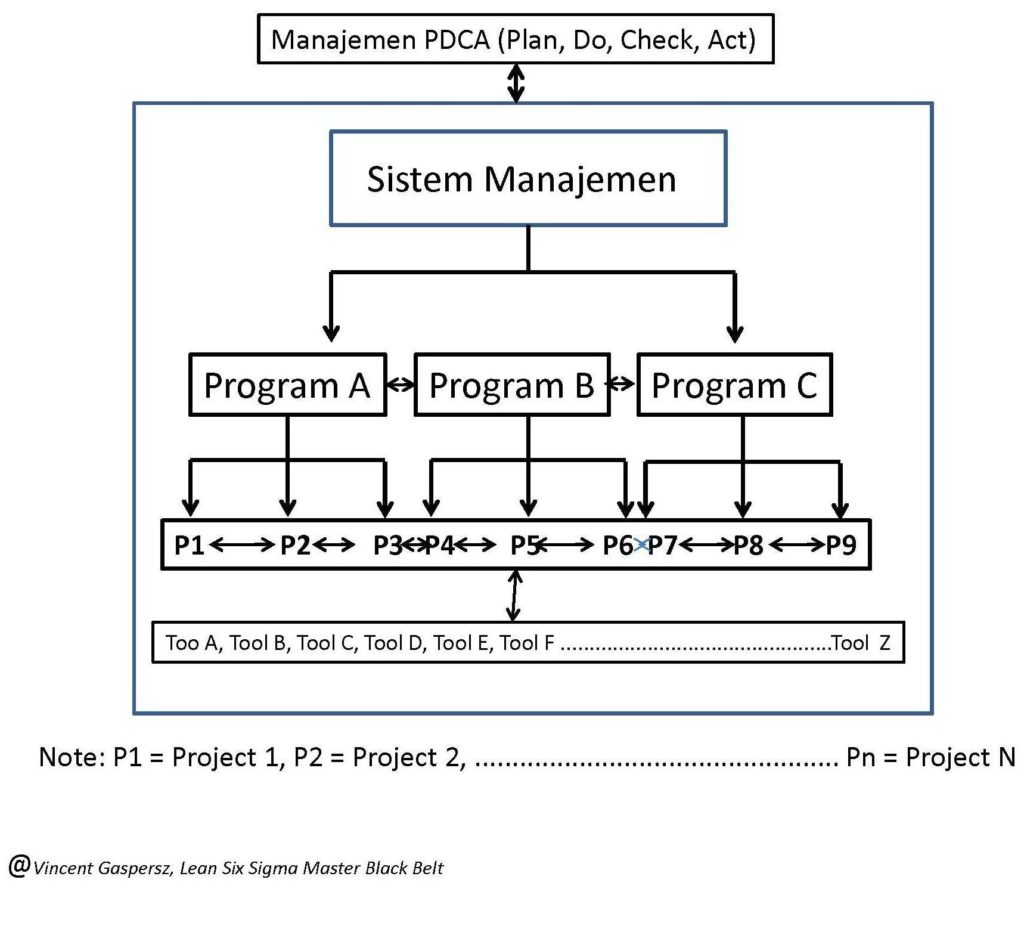
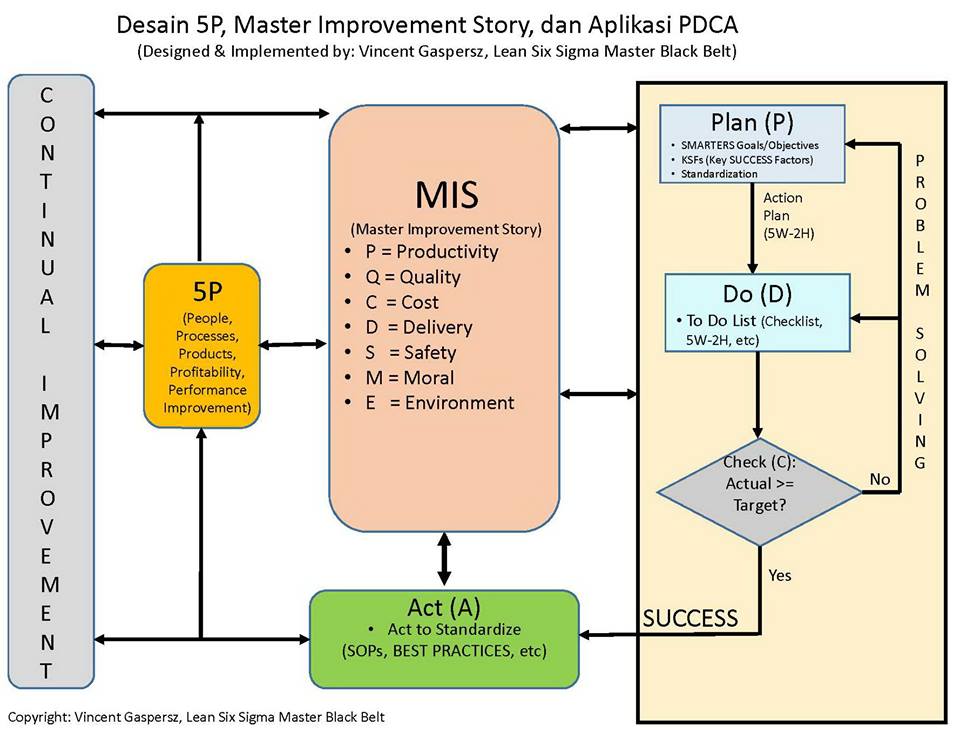
Dalam tulisan yang lalu saya telah memperkenalkan PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) berbentuk kotak yang berisi “ruang kosong”, di mana segala sesuatu yang berkaitan dengan manajemen modern atau apa saja dapat diisi dalam “ruang kosong” itu (lihat Bagan 1: PDCA Management Framework).
Tulisan berikut akan membahas bagaimana kita membangun bisnis yang SUCCESS menggunakan PDCA Approach seperti ditunjukkan dalam Bagan 2 terlampir. Tulisan ini ditujukan kepada mereka yang berfungsi sebagai entrepreneur maupun intrapreneur.
Entrepreneur atau yang sering diterjemahkan sebagai wirausaha adalah orang yang memulai bisnis sendiri dengan ide dan/atau konsep baru atau yang telah ada, sedangkan intrapreneur merupakan karyawan yang mempromosikan inovasi dalam batas-batas organisasi.
Beberapa perbedaan antara entrepreneur dan intrapreneur, adalah:
- Entrepreneur menggunakan sumber daya yang dimiliki sendiri, sedangkan intrapreneur menggunakan sumber daya yang diberikan oleh perusahaan.
- Entrepreneur menciptakan posisi yang memimpin di pasar, sedangkan intrapreneur mengubah dan memperbaharui sistem dan kultur organisasi.
- Entrepreneur mendirikan perusahaan baru, sedangkan intrapreneur bekerja pada perusahaan yang telah ada.
- Entrepreneur menggunakan modal sendiri dan/atau pinjaman modal dari bank, sedangkan intrapreneur menggunakan modal yang dibiayai oleh perusahaan.
- Entrepreneur mengambil risiko atas diri mereka sendiri dalam berinvestasi, sedangkan intrapreneur membebankan risiko kepada perusahaan di mana mereka bekerja.
Banyak calon karyawan dalam dunia bisnis terutama yang berasal dari lulusan perguruan tinggi TIDAK memiliki fungsi sebagai intrapreneur sehingga menjadi “bingung” (tidak siap) ketika memasuki dunia bisnis pertama kali. Tulisan ini diharapkan akan memberikan wawasan baik kepada entrepreneur maupun intrapreneur.
Dalam dunia bisnis, apapun jenis bisnis (industri jasa maupun manufaktur), apapun skala usaha (kecil, menengah, besar), apapun lingkup operasional (lokal, nasional, regional, global) akan menghadapi masalah besar apabila TIDAK memahami dan berorientasi pada model 5P dalam bisnis.
Model bisnis selalu berorientasi pada prinsip-prinsip 5P, sebagai berikut:
- Profitability, kemampuan menghasilkan laba perusahaan, yang menunjukkan bahwa bisnis itu unggul (Business Excellence) akan meningkat terus-menerus, apabila kinerja produk (barang dan/atau jasa) itu unggul (Product Excellence) sesuai dengan atau melebihi kebutuhan pasar dan pelanggan,
- Product (barang dan/atau jasa) akan meningkat keunggulan kinerjanya (Product Excellence) apabila kapabilitas proses yang menghasilkan produk itu unggul (Process Excellence),
- Process, akan mencapai keunggulan kinerja (Process Excellence), hanya apabila dilakukan peningkatan atau perbaikan proses terus-menerus melalui program keunggulan kinerja (Performance Excellence Program).
- Program (Performance Excellence Program) akan berhasil, hanya apabila dilakukan oleh orang-orang unggul dalam perusahaan (People Excellence),
- People, orang-orang akan mencapai keunggulan kinerja (People Excellence), hanya apabila mereka meningkatkan pembelajaran dan pertumbuhan (learning and growth) tentang konsep, metode dan alat-alat yang dipergunakan dalam solusi masalah kinerja maupun perbaikan terus-menerus untuk mencapai keunggulan proses dalam bisnis itu.
Dari model 5P di atas, kita mengetahui bahwa suatu bisnis yang maju atau unggul akan sangat tergantung pada people excellence yang berada dalam bisnis itu. Kompetisi bisnis BUKAN pada produk (barang dan/atau jasa) yang ditawarkan TETAPI kompetisi pada people (orang-orang) yang melakukan perbaikan proses terus-menerus untuk menghasilkan produk (barang dan/atau jasa) yang unggul yang memuaskan pelanggan dan pasar sekaligus pada saat yang sama meningkatkan profitabilitas perusahaan terus-menerus.
Berdasarkan model 5P di atas, kita dapat membayangkan orang-orang macam apa yang akan berkompetisi dalam memperbaiki proses bisnis terus-menerus, apabila mereka TIDAK memiliki sifat-sifat sebagai entrepreneur (pengusaha) dan intrapreneur (professional dalam perusahaan bisnis).
Sekolah-sekolah bisnis yang profesional akan membekali lulusan mereka dengan sifat-sifat entrepreneur (menjadi pengusaha bisnis mandiri) maupun intrapreneur (menjadi profesional dalam perusahaan bisnis) berlandaskan pada model 5P yang mengisi “ruang kosong” dalam kerangka manajemen PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) seperti ditunjukkan dalam Bagan 2 terlampir.
Orang-orang dalam dunia bisnis, apakah berfungsi sebagai entrepreneur (pengusaha) dan/atau intrapreneur (profesional yang mengelola bisnis), setelah memahami model 5P dalam bisnis, maka mereka HARUS menciptakan “lapangan permainan (playing field)” yang saya sebut sebagai Master Improvement Story (MIS).
TANPA Master Improvement Story (MIS) dapat diibaratkan seperti kita bermain bola TANPA tiang gawang sehingga hanya berfokus pada aktivitas “mengejar bola” dan asal “menendang bola” saja. Atau jika ada program perbaikan, maka dapat dipastikan itu merupakan program-program perbaikan secara acak (random improvement programs) BUKAN program perbaikan sistematik (systematic improvement programs).
Master Improvement Story (MIS) adalah suatu kerangka kerja (framework), peta jalan (roadmap) dari perusahaan, yang berisi: Visi, Misi, Nilai-nilai, Perspektif Bisnis, Sasaran dan Tujuan Strategik, Indikator-indikator Kinerja Kunci (KPIs), Program-program Peningkatan Keunggulan Kinerja (Performance Excellence Programs) yang disusun secara SISTEMATIK beserta Rencana-rencana Tindakan (Action Plans), yang menjadi panduan bagi manajemen dalam merencanakan, menerapkan, dan mengendalikan kebijakan-kebijakan strategik perusahaan dalam kerangka sistem secara terintegrasi menuju Keunggulan Bisnis (Business Excellence).
Jika organisasi memiliki beberapa unit-unit bisnis strategik (Strategic Business Units = SBUs), maka Master Improvement Story dapat didesain pertama kali pada tingkat korporat (corporate level), baru kemudian dijabarkan atau disebarluaskan ke unit-unit bisnis strategik. Master Improvement Story pada tingkat korporat, sering disebut sebagai: Corporate Master Improvement Story (Corporate MIS), sedangkan Master Improvement Story pada tingkat unit-unit bisnis strategik, disebut sebagai Strategic Business Unit’s Master Improvement Story (SBU’s MIS).
Semua kebijakan dan keputusan operasional manajemen dari unit-unit bisnis strategik (SBUs MIS) harus mendukung Corporate Master Improvement Story (Corporate MIS).
Manajemen puncak (top management) harus bertanggung jawab mengembangkan Master Improvement Story, melalui merumuskan Visi, Misi, Nilai-nilai Organisasi, Sasaran Jangka Panjang (long-term goals, 3-5 tahun), Tujuan-tujuan Jangka Pendek (annual objectives, 1 tahun) yang diturunkan dari sasaran jangka panjang (long-term goals), Indikator-indikator Kinerja Kunci (key performance indicators = KPIs), target kinerja selama satu tahun (annual performance targets), dan mengendalikan Program-program Peningkatan Keunggulan Kinerja (Performance Excellence Programs) yang tercantum dalam Master Improvement Story perusahaan itu. Setiap Program Peningkatan Keunggulan Kinerja harus memiliki Rencana Tindakan (action plans), agar memudahkan dalam eksekusi program-program menuju keunggulan bisnis (business excellence) itu.
Semua yang dijelaskan dalam Master Improvement Story (MIS) itu akan dikendalikan menggunakan kerangka manajemen PDCA seperti ditunjukkan dalam Bagan 2.
Indikator-indikator kinerja kunci (KPIs) yang HARUS dipertimbangkan untuk direncanakan, dimonitor, dan dikendalikan adalah berkaitan dengan elemen-elemen dalam model bisnis 5P, yaitu:
- Elemen Profitability (kemampuan menghasilkan laba) dalam model bisnis 5P akan ditingkatkan terus-menerus melalui peningkatan terus-menerus Productivity (P) dan Quality (Q). Dapat ditunjukkan bahwa Profitability = TR / TC = (po x O) / (pi x I) = (po / pi) x (O / I); di mana po dan pi adalah harga dari output (po) dan harga dari input (pi), sedangkan O adalah Output dan I adalah Input dalam sistem bisnis. Besaran (O / I) dinamakan Productivity yang bersifat Controllable oleh manajemen bisnis, sedangkan besaran (po / pi) bersifat Uncontrollable BUT Predictable oleh manajemen bisnis melalui Quality (Q) dari produk (barang dan/atau jasa). Dengan demikian dapat dituliskan formula: Profitability = Productivity x Quality = P x Q.
- Elemen Product Excellence dapat diwakili melalui peningkatan Quality (Q) dari produk (barang dan/atau jasa). Sehingga perencanaan, monitoring, dan pengendalian kinerja Productivity (P) dan Quality (Q) dalam sistem bisnis akan mampu meningkatkan sekaligus kepuasan pelanggan/pasar dan pemegang saham (shareholders).
- Elemen Process Excellence (keunggulan proses bisnis) akan meningkat apabila kita mampu meningkatkan kinerja Productivity (P), Quality (Q), Cost Effectiveness (C), Delivery (D), Safety (S), Moral (M), and Environment (E). Dalam bisnis manufaktur kita dapat memperkenalkan dua indikator kinerja kunci (KPIs) yang bersifat komposit, yaitu: (1) OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) = Availability (A) x Productivity (P) x Quality (Q), di mana: A = waktu ketersediaan operasional mesin-mesin, P = Produktivitas mesin-mesin, dan Q = kualitas dari produk (barang dan/atau jasa) yang dihasilkan dari mesin-mesin dan/atau peralatan, dan (2) OLE (Overall Labor Effectiveness) = Availability (A) x Productivity (P) x Quality (Q), di mana A = waktu kehadiran dari tenaga kerja, P = produktivitas tenaga kerja, dan Q = kualitas output atau produk (barang dan/atau jasa) yang dihasilkan oleh tenaga kerja.
- Elemen People Excellence (keunggulan orang-orang) akan meningkat apabila kita mampu meningkatkan semangat atau Moral (M) karyawan melalui proses pembelajaran dan pertumbuhan (Learning & Growth).
- Elemen Performance Excellence Program (program-program keunggulan kinerja) merupakan suatu keniscayaan dalam dunia bisnis masa sekarang dan yang akan datang agar meningkatkan daya saing bisnis dan industri.
Dari uraian di atas kita akan bertanya apakah lulusan perguruan tinggi di Indonesia akan mampu memenuhi pasar tenaga kerja dalam dunia bisnis dan industri di Indonesia maupun global?
Jawaban akan tergantung pada sejauh mana pemahaman pengelola perguruan tinggi di Indonesia dalam memenuhi kebutuhan dunia bisnis dan industri di Indonesia maupun global.
Jika dunia perguruan tinggi di Indonesia TIDAK mengantisipasi hal ini, maka merupakan suatu keniscayaan bahwa tenaga-tenaga kerja yang produktif dan berkualitas dari luar negeri yang akan mengisi pasar tenaga kerja bisnis dan industri di Indonesia sesuai dengan mekanisme yang berlaku dalam pasar yang terbuka, yaitu: sistem bisnis dan industri di negara-negara yang memiliki produktivitas dan kualitas yang lebih tinggi akan mengalir menuju sistem bisnis dan industri di negara-negara yang memiliki produktivitas dan kualitas yang lebih rendah, mengikuti hukum air yang mengalir dari dataran tinggi menuju dataran rendah.
Tulisan saya mendatang akan membahas bagaimana mekanisme PDCA Management Framework sebagai “kartu Joker” memainkan peranan penting bagi pemula yang membangun karier profesional di bidang bisnis dan industri, baik pada perusahaan-perusahaan nasional maupun multinasional (MNCs = Multi National Companies).
Tks. Salam SUCCESS.
Building SUCCESSFUL Business Using the PDCA Management Framework
By: Vincent Gaspersz, Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt
American Society for Quality (www.asq.org) CMQ/OE, CQA, CSSBB, CQE, CQIA
American Production and Inventory Control Society (www.apics.org) CFPIM, CSCP
International Quality Federation (www.iqf.org) Six Sigma Master Black Belt
Registration Accreditation Board (www.exemplarglobal.org) Quality Management System Practitioner
In the previous article, I introduce the box-shaped PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) containing “empty space”, where everything associated with modern management or whatever can be filled in that “empty space” (see Chart 1 above: PDCA Management Framework).
The following article will discuss how we build a SUCCESSFUL business using PDCA Approach as shown in Chart 2 below. This article is addressed for those who function as entrepreneurs or intrapreneurs.

Entrepreneur or is someone who starts his/her own business with new or existing ideas and/or concepts, while intrapreneur is an employee who promotes innovation within the boundaries of the organization.
Some of the differences between entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs, are:
- Entrepreneur uses the resources owned by him/herself, while intrapreneur uses resources provided by the company.
- Entrepreneur creates a leading position in the market, while intrapreneur changes and updates the organization’s system and culture.
- Entrepreneur founded a new company, while intrapreneur works on an existing company
- ntrepreneur uses his/her own capital and/or loan capital from the bank, while intrapreneur uses the company’s funded capital.
- Entrepreneur takes risks upon him/herself in investing, while intrapreneur imposes the risk to the company where he/she works.
Many prospective employees in the business world, especially coming from university graduates, do NOT have the function as intrapreneurs so that they become “confused” (not ready) when entering the business world for the first time. This article will hopefully provide good insight for both the entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs.
In the business world, any type of business (service or manufacturing industry), any scale of business (small, medium, large), any operational scope (local, national, regional, global) will face a big problem if it does NOT understand and is NOT oriented towards 5P model in business.
Business model is always oriented on 5P principles, as follows:
- Profitability, the ability to generate profits for the company, which shows that the business is excellent (Business Excellence) and will increase continuously, if the performance of products (goods and/or services) is excellent (Product Excellence) matching or exceeding the market and customer needs,
- Products (goods and/or services) will increase in their performance excellence (Product Excellence) when the process capability that produces those products are excellent (Process Excellence)
- Process will achieve performance excellence (Process Excellence), only when there are continous processs increase or improvement done through Performance Excellence Program.
- Program (Performance Excellence Program) will succeed only if it is done by excellent people in the company (People Excellence),
- People, people will achieve performance excellence (People Excellence), only if they improve learning and growth about the concepts, methods, and tools used in the problem solving performance and continuous improvement to achieve process excellence in that business.
From the 5P model above, we know that an advanced or excellent business will largely depend on the people excellence in that business. Business competition is NOT on the products (goods and/or services) offered BUT the competition on people who are doing continuous process improvement in order to produce excellent products (goods and/or services) that satisfy customers and market while at the same time continuously enhancing the profitability of the company.
Based on the 5P model above, we can imagine what sort of people who will compete in improving continuous business processes, if they do NOT have the characters as entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs (professionals in business enterprises).
Professional business schools will equip their graduates with the entrepreneurial (being independent business entrepreneur) and intrapreneurial (being professional within company) characters based on the 5P model, which fills the “empty space” within the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) management framework as shown in Chart 2 attached above.
People in the business world, whether functioning as entrepreneurs and/or intrapreneurs (professionals who manage businesses), after understanding the 5P model in the business, then they MUST create a “playing field” that I call the Master Improvement Story (MIS).
WITHOUT Master Improvement Story (MIS), it can be likened to as if we play football WITHOUT the goalposts so that we only focus on the activity of just “running after the ball” and “kicking the ball” for no reason. Or if there is an improvement program, it can be ascertained that that improvement program is a random improvement programs, NOT a systematic improvement program.
Master Improvement Story (MIS) is a framework, the roadmap of the company, which includes: Vision, Mission, Values, Business Perspective, Goals and Strategic Objectives, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and Performance Excellence Programs that are arranged SYSTEMATICALLY along with Action Plans. MIS serves as a guide for management in planning, implementing, and controlling the company’s strategic policies within the system framework integratively toward Business Excellence.
If an organization has several Strategic Business Units = SBUs, then the Master Improvement Story can be designed first at the corporate level, and then translated or disseminated to the strategic business units. Master Improvement Story at the corporate level, is often referred to as: Corporate Master Improvement Story (Corporate MIS), while Master Improvement Story at the level of the strategic business units, is referred to as a Strategic Business Unit’s Master Improvement Story (SBU’s MIS).
All policies and operational management decisions from the strategic business units (SBUs MIS) should support the Corporate Master Improvement Story (Corporate MIS).
The top management should be responsible for developing the Master Improvement Story, by formulating the Vision, Mission, Organization’s Values, Long-Term Goal (3-5 years), Short-Term Goals (annual objectives, 1 year) derived from long-term goals, Key Performance Indicators = KPIs, performance targets for one year (annual performance targets), and controlling Performance Excellence Programs that are listed in that company’s Master Improvement Story. Each Performance Improvement Excellence Program must have an Action Plan in order to facilitate the execution of programs towards that business excellence.
All that is described in that Master Improvement Story (MIS) will be controlled using PDCA management framework as shown in Chart 2 above.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that MUST be considered to be planned, monitored, and controlled are related to the elements in 5P business model, namely:
- Profitability element (ability to generate profits) in 5P business model will be improved constantly through continuous improvement of Productivity (P) and Quality (Q). It can be shown that Profitability = TR / TC = (po x O) / (pi x I) = (po / pi) x (O / I); where po and pi are the price of output (po) and the price of the input (pi), whereas O is the Output and I is the Input in business systems. The amount of (O / I) is called the Productivity that is Controllable by nature by the business management, while the amount of (po / pi) is Uncontrollable BUT Predictable by the business management via Quality (Q) of products (goods and/or services). Thus, it can be written the formula: Profitability = Productivity x Quality = P x Q.
- Product Excellence element can be represented through Quality (Q) improvement from the products (goods and/or services). So that the planning, monitoring, and controlling of the performance of Productivity (P) and Quality (Q) in the business system will be able to simultaneously increase the satisfaction of customers, market, and shareholders.
- Process Excellence element will increase if we are able to improve the performance of Productivity (P), Quality (Q), Cost Effectiveness (C), Delivery (D), Safety (S), Moral (M), and Environment (E ). In the manufacturing business, we can introduce two key performance indicators (KPIs) that are composite, namely: (1) OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) = Availability (A) x Productivity (P) x Quality (Q), where: A = the operational time availability of the machines, P = Productivity of the machines, and Q = the quality of the products (goods and/or services) generated from the machines and/or equipment, and (2) OLE (Overall Labor Effectiveness) = Availability (A) x Productivity (P) x Quality (Q), where A = attendance time of the workforce, P = the productivity of the workforce, and Q = quality of the output or products (goods and/or services) generated by the workforce.
- People Excellence element will increase if we are able to increase the spirit or morale (M) of the employees through the process of Learning & Growth.
- Performance Excellence Program element is a necessity in the business world today and in the future in order to improve the competitiveness of business and industry.
From the above, we will ask whether university graduates in Indonesia will be able to meet the labor market in the world of business and industry in Indonesia and globally?
The answer will depend on the extent of the Indonesian higher education managers’ understanding in meeting the needs of business and industry in Indonesia and globally.
If the higher education world in Indonesia does NOT anticipate this matter, it is without doubt that productive and qualified labor force from abroad will fill the labor market of businesses and industries in Indonesia in accordance with the existing mechanisms that prevail in the open market, namely: business and industrial systems in countries that have higher productivity and quality will flow toward business and industrial systems in countries that have lower productivity and quality, following the law of water that flows from the highlands to the lowlands.
My next article will discuss how the mechanism of PDCA Management Framework as the “Joker Card” plays an important role for the beginners who build their professional careers in business and industry, whether in national or multinational companies (MNCs = Multi National Companies).
Thank you. Best Regards for SUCCESS.