-
Bahasa Indonesia
-
English
Oleh: Vincent Gaspersz, Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt
American Society for Quality (www.asq.org) CMQ/OE, CQA, CSSBB, CQE, CQIA
American Production and Inventory Control Society (www.apics.org) CFPIM, CSCP
International Quality Federation (www.iqf.org) Six Sigma Master Black Belt
Registration Accreditation Board (www.exemplarglobal.org) Quality Management System Lead Specialist
Untuk memahami bagaimana mengelola sistem-sistem manajemen internasional, maka perlu dikemukakan terlebih dahulu terminologi dan definisi secara struktural mulai dari manajemen (management), sistem manajemen (management system), program (programme), proyek (project), dan peralatan (tool) agar JANGAN sampai terjadi mereka yang belajar ilmu manajemen membuat kesalahan dan asal mengucapkan istilah-istilah penting itu tetapi TIDAK memahaminya.
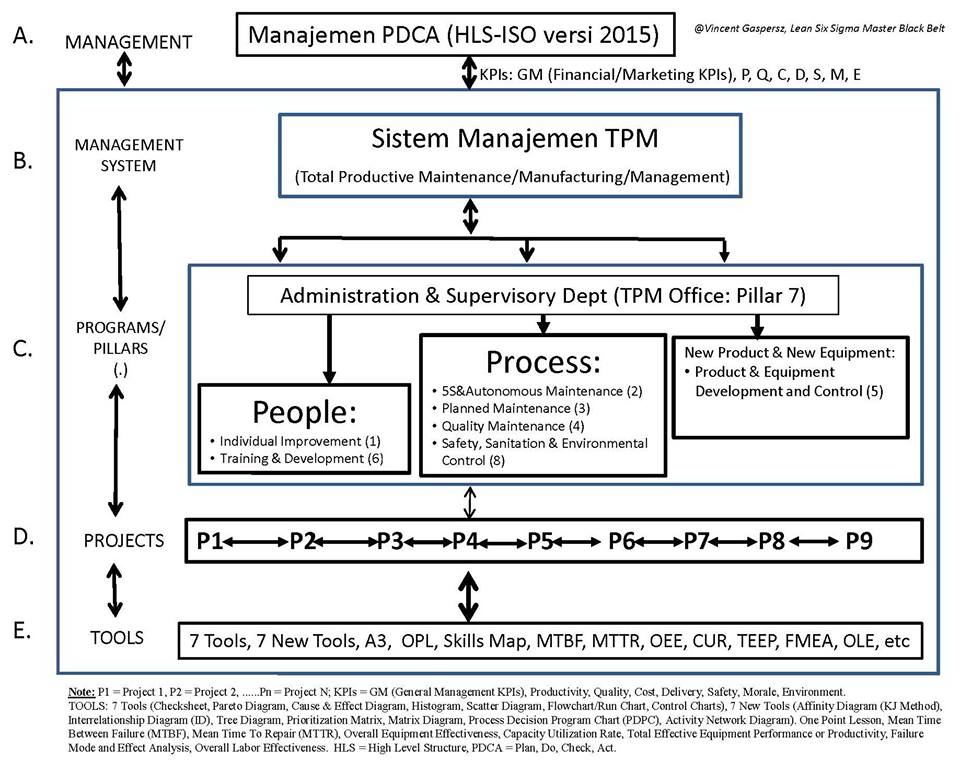
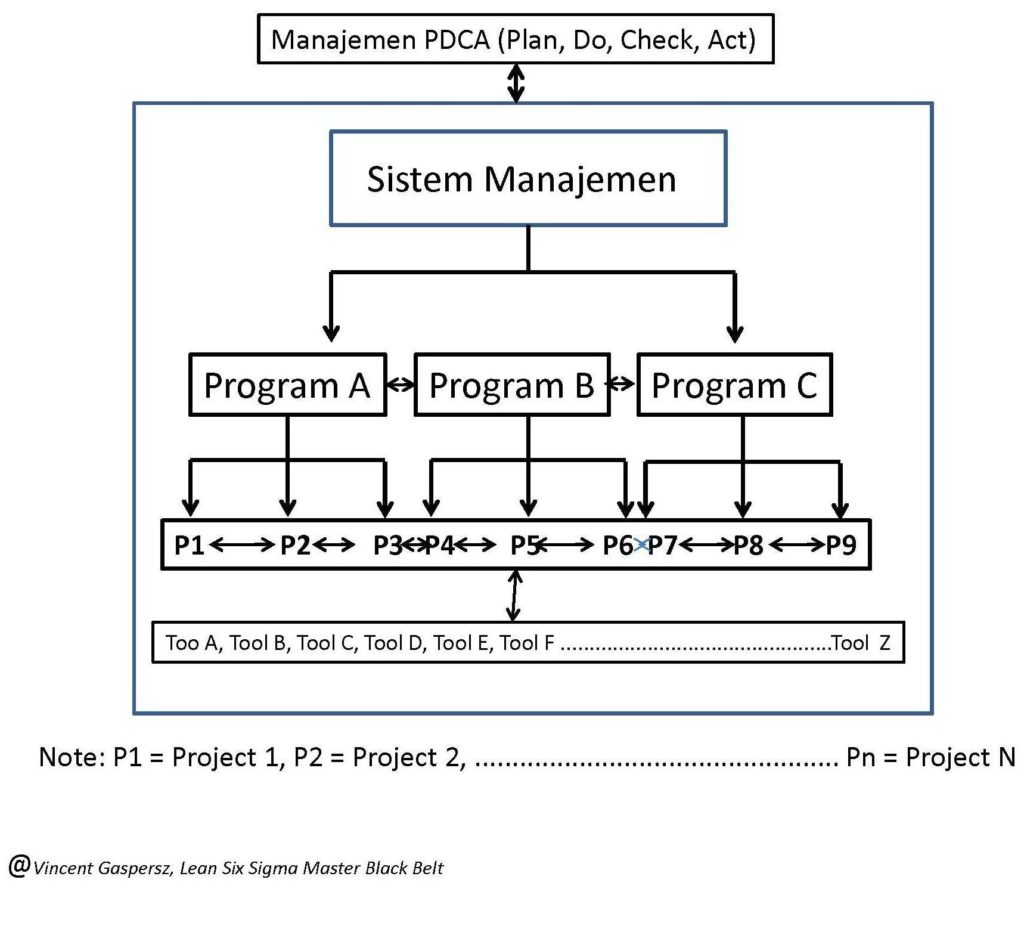
Agar memudahkan penjelasan, maka ditampilkan bagan terlampir beserta nomor kode A, B, C, D, dan E. Contoh sistem manajemen yang ditampilkan adalah Sistem Keunggulan Kinerja TPM (Total Productive Maintenance/Manufacturing/Management). TPM Performance Excellence System dipublikasikan oleh JIPM–the Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance (www.jipm.or.jp/en).
Sistem-sistem manajemen internasional lain yang dikenal publik internasional adalah ISO yang dipublikasikan oleh the Internasional Organization for Standardization (www.iso.org), Malcolm Baldrige Criteria for Performance Excellence (MBCfPE) yang dipublikasikan oleh NIST—National Institute of Standards and Technology (www.nist.gov) yang merupakan organisasi di bawah pemerintah USA, dan lain-lain.
- Manajemen (Management) adalah fungsi-fungsi PDCA: Plan-Perencanaan, Do-Pelaksanaan, Check-Pemeriksaan, dan Act-Penindakan untuk pembuatan keputusan pengendalian, apakah kita akan melakukan tindakan korektif (solusi masalah) atau melakukan standardisasi praktek-praktek terbaik (best practices) untuk peningkatan terus-menerus dan/atau inovasi. Dalam organisasi Lean Six Sigma, manajemen adalah fungsi-fungsi DMAIC: Mendefinisikan (Define), Mengukur (Measure), Menganalisis (Analyze), Meningkatkan atau Memperbaiki (Improve), dan Mengendalikan (Control). Untuk Design for Lean Six Sigma, maka manajemen adalah fungsi-fungsi DMADV: Mendefinisikan (Define), Mengukur (Measure), Menganalisis (Analyze), Mendesain (Design), dan Memverifikasi (Verify).
- Sistem Manajemen (Management System) adalah kerangka kerja yang mencakup kebijakan-kebijakan, proses-proses dan prosedur-prosedur yang digunakan oleh suatu organisasi untuk menjamin bahwa sistem manajemen itu dapat memenuhi semua tugas-tugas yang diperlukan agar mencapai tujuan organisasi. Menurut ISO (www.iso.org) Sistem Manajemen memungkinkan organisasi menerapkan pendekatan terstruktur terhadap aktivitas-aktivitas organisasi agar mencapai tujuan organisasi itu. Contoh: Sistem Manajemen TPM (Total Productive Maintenance/Manufacturing/Management), Sistem Manajemen Kualitas ISO 9001:2015, Sistem Manajemen Lingkungan ISO 14001:2015, Sistem Manajemen Risiko ISO 31000:2009, dll.
- Program (Programme) adalah kelompok proyek-proyek yang saling berkaitan satu sama lain yang dikelola dengan cara terkoordinasi untuk memperoleh manfaat-manfaat, di mana hal ini tidak mungkin diperoleh dari manajemen proyek secara terpisah atau parsial. Contoh: Program Pengembangan Sumber Daya Manusia (Human Resource Development Program), Program Pengembangan Kepemimpinan (Leadership Development Program), dll.
- Proyek (Project) adalah aktivitas-aktivitas spesifik yang memiliki batas waktu memulai dan berakhir ketika tujuan spesifik itu telah tercapai. Contoh: Proyek Pembuatan Software Komputer, Proyek Pembangunan Gedung, dll.
- Peralatan (Tool) adalah suatu item yang digunakan untuk tujuan tertentu atau spesifik. Suatu peralatan dapat berupa obyek fisik seperti peralatan mekanik (misal: palu, gergaji, dll) atau obyek teknikal seperti program komputer, file, dll. Dalam statistika, peralatan statistikal (statistical tool) digunakan untuk menganalisis data yang dikumpulkan berdasarkan pengukuran pada fakta untuk menghasilkan informasi statistik. Perangkat lunak statistikal (statistical softwares) seperti: SPSS/MINITAB/AMOS, dll digolongkan sebagai Statistical Tools. Contoh: Seven Basic Quality Tools (Check sheet, Pareto Diagram, Cause & Effect Diagram, Histogram, Scatter Diagram, Flow chart/Run Chart/Stratification, Control Charts), Seven Management & Planning Tools (Affinity Diagram–KJ Method), Interrelationship Diagram (ID), Tree Diagram, Prioritization Matrix, Matrix Diagram, Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC), Activity Network Diagram (AND), dll.
Salam SUCCESS.
Terminology and Definitions of Management, Systems Management, Programme, Project and Tool (Series 1: Managing International Management Systems)
By: Vincent Gaspersz, Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt
American Society for Quality (www.asq.org) CMQ/OE, CQA, CSSBB, CQE, CQIA
American Production and Inventory Control Society (www.apics.org) CFPIM, CSCP
International Quality Federation (www.iqf.org) Six Sigma Master Black Belt
Registration Accreditation Board (www.exemplarglobal.org) Quality Management System Lead Specialist
To understand how to manage international management systems, it is necessary to state the terminology and structural definitions starting from management, management system, program, project, and tool, so that IT DOES NOT occur that those who study management make the mistake of uttering those important terms, but do NOT understand them.
In order to facilitate the explanation, the attached chart above is shown along with the code numbers: A, B, C, D, and E. The example of management systems shown is TPM (Total Productive Maintenance/Manufacturing/ Management) Performance Excellence System. TPM Performance Excellence System is published by JIPM – the Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance (www.jipm.or.jp/en).
Other international management systems known to the international public are ISO published by the International Organization for Standardization (www.iso.org), Malcolm Baldrige Criteria for Performance Excellence (MBCfPE) published by NIST-National Institute of Standards and Technology (www .nist.gov) which is an organization under U.S. government, and others.
- Management is the PDCA functions: Plan, Do, Check, and Act for control decision making, whether we will take corrective action (problem solving) or standardize best practices for continuous improvement and/or innovation. In Lean Six Sigma organization, management is the DMAIC functions: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. For Design for Lean Six Sigma, management is the DMADV functions: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify.
- Management System is a framework that includes the policies, processes and procedures that are used by an organization to ensure that management system can meet all the tasks required to achieve the organization’s goal. According to ISO (www.iso.org), Management System enables organization to apply structured approach to its organizational activities in order to achieve that organization’s goal. Examples: TPM (Total Productive Maintenance/Manufacturing/Management) Management System, ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System, ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management System, ISO 31000:2009 Risk Management System, etc.
- Programme is a group of interrelated projects coordinatedly managed in order to obtain benefits, where such benefits are not possible to be obtained from separate or partial project management. Examples: Human Resource Development Program, Leadership Development Program, etc.
- Projects are specific activities that have starting and ending time limit when that specific objective has been reached. Examples: Computer Software Development Project, Building Construction Project, etc.
- Tool is an item that is used for a particular or specific purpose. A tool can be of physical objects such as mechanical equipment (e.g. hammers, saws, etc.) or of technical objects such as computer programs, files, etc. In statistics, statistical tool is used to analyze data collected based on the measurements on facts to produce statistical information. Statistical softwares, such as: SPSS/MINITAB/AMOS, etc., are classified as Statistical Tools. Examples: Seven Basic Quality Tools (Check sheet, Pareto Diagram, Cause & Effect Diagram, Histogram, Scatter Diagram, Flow chart/Run Chart/Stratification, Control Chart), Seven Management & Planning Tools (Affinity Diagram – KJ Method), Interrelationship Diagrams (ID), Tree Diagrams, Prioritization Matrix, Matrix Diagrams, Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC), Activity Network Diagrams (AND), etc.
Best Regards for SUCCESS.